
When it comes to improving your home’s energy efficiency, window glazing plays a pivotal role. Windows are often seen as the gateway to natural light and fresh air, but they can also be a significant source of energy loss if not properly designed. Understanding the role of window glazing in your home’s energy efficiency can help you make informed choices that lead to lower energy bills, enhanced comfort, and a reduced carbon footprint.
What is Window Glazing?
Window glazing refers to the glass installed within a window frame. The term can also describe the process of securing the glass in place. However, in the context of energy efficiency, window glazing usually pertains to the type and configuration of glass panes used in a window. There are several glazing options available, each with different levels of insulation and energy efficiency:
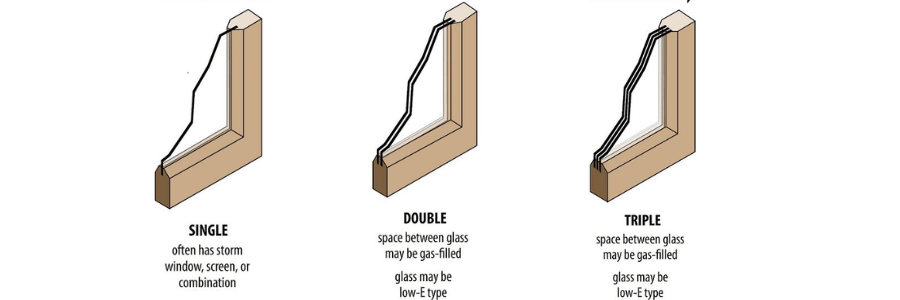
- Single Glazing: A single layer of glass that offers minimal insulation. While single-glazed windows allow for maximum natural light, they provide little to no protection against heat loss or gain.
- Double Glazing: Consists of two layers of glass separated by a space filled with air or an inert gas like argon. Double glazing significantly improves insulation and reduces energy transfer, making it the most common choice for energy-efficient windows.
- Triple Glazing: Incorporates three layers of glass, with two insulating spaces. Triple glazing provides the highest level of insulation, making it ideal for extreme climates or homes where energy efficiency is a top priority.
How Window Glazing Impacts Energy Efficiency
The efficiency of window glazing is primarily determined by its ability to minimize heat transfer. This involves both preventing heat from escaping your home in the winter and blocking it from entering during the summer. Here’s how different types of glazing contribute to energy efficiency:
Insulation: Double and triple glazing create a barrier between the inside and outside environments. The air or gas-filled space between the panes acts as an insulator, reducing the rate at which heat passes through the glass. This means your home stays warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer, reducing the need for artificial heating and cooling.
Thermal Break: Modern glazing techniques often incorporate a thermal break—a non-conductive material placed between layers of glass or within the frame itself. This feature prevents heat from being conducted through the window frame, further enhancing insulation.
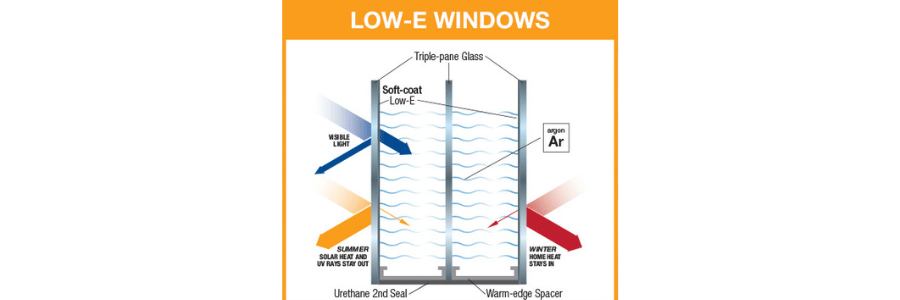
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC): The SHGC measures how much solar radiation is transmitted through the window. Lower SHGC values indicate that less solar heat enters your home, which is particularly beneficial in hot climates. Glazing options with Low-E (Low Emissivity) coatings can help control SHGC, allowing light to pass through while reflecting heat back out.
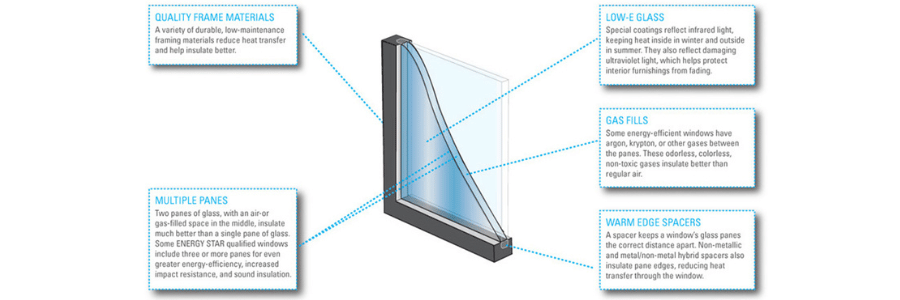
Types of Energy-Efficient Glazing
To maximize energy efficiency, it’s essential to choose the right type of glazing for your home’s specific needs. Here are some popular energy-efficient glazing options:
Low-E Glass: Low-E glass features a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared heat. During the winter, it keeps heat inside, and in the summer, it reflects heat away from your home. Low-E glass also blocks harmful UV rays, which can fade furniture and flooring.
Gas-Filled Glazing: Inert gases like argon or krypton are often used between the panes in double or triple glazing. These gases are denser than air, providing better insulation without compromising clarity or light transmission.
Laminated Glass: While primarily used for security and soundproofing, laminated glass can also contribute to energy efficiency. It consists of two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer that holds the panes together. This design can improve insulation and reduce heat transfer.
Choosing the Right Glazing for Your Home
Selecting the right glazing depends on various factors, including your climate, budget, and the specific needs of your home. Here are a few tips to guide your decision:
Consider Your Climate: If you live in a colder region, double or triple glazing with a low U-factor (a measure of heat loss) is essential for retaining warmth. In warmer climates, focus on glazing with a low SHGC to reduce heat gain.
Assess Your Home’s Design: Large windows or those facing direct sunlight may require more advanced glazing options, such as Low-E or tinted glass, to balance light and heat.
Think Long-Term: While energy-efficient glazing options might have a higher upfront cost, they can lead to substantial savings on your energy bills over time. Additionally, investing in high-quality glazing can increase your home’s value and reduce its environmental impact.

Conclusion
Window glazing is more than just a finishing touch—it’s a crucial element in your home’s energy efficiency. By understanding the different types of glazing and how they impact insulation, heat transfer, and overall comfort, you can make informed decisions that benefit both your wallet and the environment.
Whether you’re building a new home or upgrading your current windows, choosing energy-efficient glazing is a smart investment that pays off in both comfort and cost savings. By selecting the right glazing for your needs, you’ll not only enhance the beauty of your home but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Looking to upgrade your home’s energy efficiency with the right window glazing? Explore our advanced search tool to compare a wide range of glazing options and window styles from top manufacturers. Whether you’re seeking better insulation, reduced energy bills, or enhanced comfort, our search feature makes it easy to find the perfect solution for your home. Start your search today and take the first step towards a more energy-efficient and comfortable living space!
Click below to begin your window glazing search!

