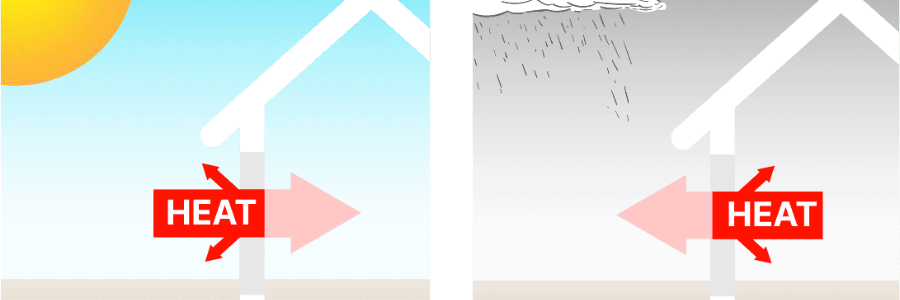
When it comes to making your home more energy-efficient, one of the most important factors to consider is the type of windows you install. While there are many aspects to look at when choosing windows—such as design, material, and cost—the window’s U-value is one of the most crucial in terms of energy performance. Understanding what U-values are, and how they affect your home’s energy efficiency, can help you make more informed decisions when selecting windows. Here’s a homeowner’s guide to understanding window U-values and how they contribute to energy-efficient glass.

What is a U-Value?
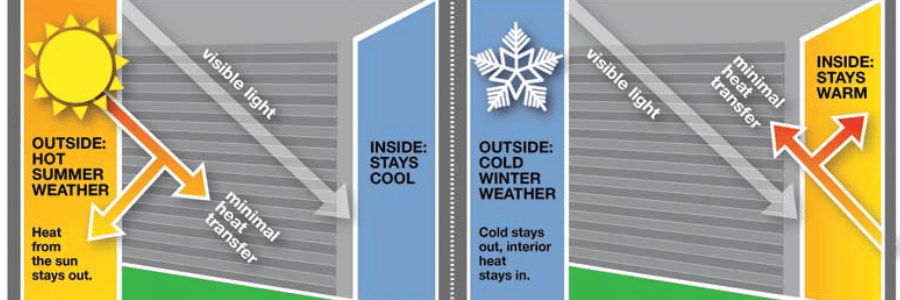
A U-value (also known as thermal transmittance) measures how well a window insulates your home. Specifically, it refers to the amount of heat that passes through the window from inside to outside (or vice versa). The lower the U-value, the better the window’s ability to prevent heat loss or gain. U-values are typically expressed in watts per square meter Kelvin (W/m²K), with lower numbers indicating better insulation.
Windows with a low U-value help keep your home warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. This not only improves comfort but also helps to lower your energy bills.
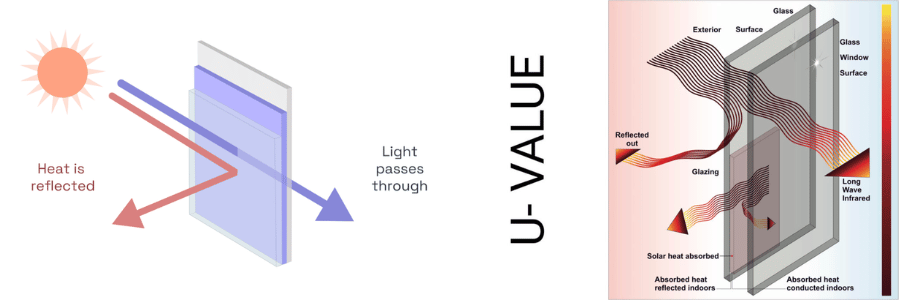
Why U-Values Matter for Energy Efficiency
U-values are important because they directly impact the energy efficiency of your home. Homes with high U-value windows lose more heat in the winter and gain more heat in the summer. This means your heating and cooling systems have to work harder, resulting in higher energy costs. In contrast, windows with low U-values provide better insulation, reducing heat loss in the colder months and minimizing heat gain when it’s hot outside.
By choosing windows with low U-values, homeowners can significantly reduce energy consumption, lower their utility bills, and enhance the comfort of their living space. Additionally, more energy-efficient windows contribute to a smaller carbon footprint by reducing the amount of energy needed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
How to Read a U-Value Rating
When shopping for windows, you’ll often see U-values listed on product labels or specifications. These values are typically displayed in watts per square meter Kelvin (W/m²K). To give you a clearer picture of what these numbers mean:
- U-Value of 1.0 W/m²K or lower: Excellent insulation, typically found in high-performance windows with multiple glazing layers, gas fills, and low-emissivity coatings.
- U-Value of 1.1 to 1.3 W/m²K: Good insulation, suitable for most residential homes, providing a balance of energy efficiency and cost.
- U-Value of 1.4 W/m²K or higher: Less efficient insulation, commonly seen in basic, single-glazed windows, which allow more heat to pass through.
It’s essential to check the U-value when comparing window products to ensure you’re choosing one that meets your energy efficiency goals.
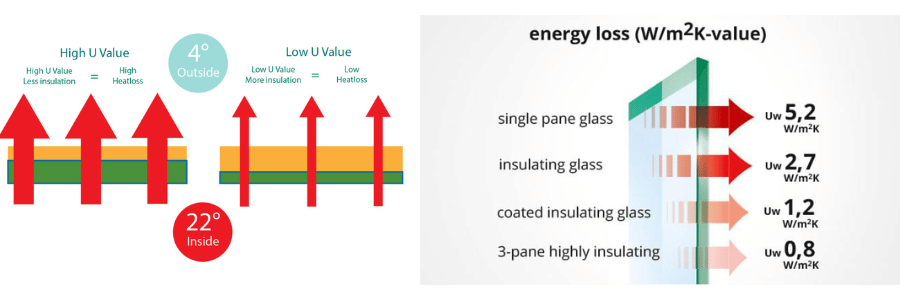
Factors that Affect U-Values
Several factors contribute to a window’s overall U-value, including the materials used in the frame, the type of glass, and the number of panes:
- Glazing: Single-glazed windows have a higher U-value than double-glazed or triple-glazed windows because single-glazed glass is a poor insulator. Double and triple glazing, where two or three layers of glass are separated by air or gas, significantly improve the U-value by reducing heat transfer.
- Gas Fill: The space between glass panes in double- or triple-glazed windows is typically filled with a gas, such as argon or krypton. These gases are less conductive than air, improving the window’s insulation properties and lowering its U-value.
- Low-Emissivity (Low-E) Coatings: Low-E coatings are thin, invisible layers of metal oxide applied to glass to reduce the amount of heat transfer through the window. They reflect infrared heat back into the room, helping to keep your home warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer. Low-E coatings can help lower a window’s U-value by enhancing its insulation.
- Frame Material: The material of the window frame also affects the U-value. Frames made from materials with low thermal conductivity, such as vinyl, fiberglass, or wood, tend to have better insulation properties. Metal frames, such as aluminum, can increase a window’s U-value unless they are thermally broken with a plastic or insulating material.
- Window Design: The overall design of the window can also influence its U-value. For instance, windows with a larger surface area or those exposed to direct sunlight for long periods may have a higher U-value if they aren’t properly insulated.
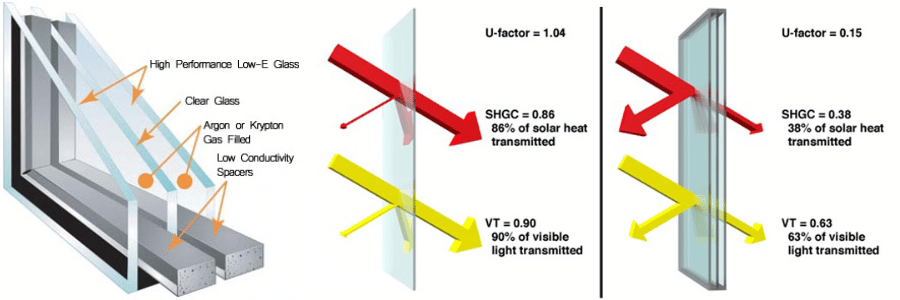
The Importance of U-Value in Different Climates
The ideal U-value for your windows can vary depending on your local climate. In colder climates, windows with a lower U-value (better insulation) are essential to prevent heat loss and reduce energy bills. In warmer climates, you’ll want to focus on windows that not only have a low U-value but also limit solar heat gain, ensuring your home stays cool without excessive reliance on air conditioning.
- Cold Climates: Opt for windows with U-values as low as possible to prevent heat loss. Double- or triple-glazed windows with gas fills and Low-E coatings are ideal.
- Warm Climates: While low U-values are still important for insulation, you should also prioritize windows with low Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) to reduce heat gain. Choose windows that offer both insulation and solar control.
How to Improve U-Value in Existing Windows
If you’re not ready to replace your windows but want to improve energy efficiency, there are a few steps you can take to improve the U-value of your current windows:
- Install window film: Low-emissivity window films can be applied to existing windows to improve insulation.
- Add storm windows: Installing storm windows over your current windows can provide an additional layer of insulation, reducing heat loss.
- Use heavy drapes or thermal curtains: Insulated window coverings can improve thermal performance by reducing heat transfer through the glass.
- Seal gaps: Caulking around the edges of your windows to prevent drafts can also help maintain energy efficiency and improve overall comfort.

Conclusion
Understanding window U-values is key to making informed decisions about the energy efficiency of your home. A lower U-value means better insulation, leading to reduced energy consumption, lower utility bills, and a more comfortable living environment. By considering factors such as glazing, gas fills, and Low-E coatings, you can select windows that enhance your home’s energy performance and reduce its environmental impact. Whether you’re building a new home or upgrading existing windows, understanding U-values will help you choose the best windows for your needs, keeping your home comfortable and energy-efficient for years to come.